Your healthcare provider can learn about your thyroid function from thyroid tests. Diagnoses for thyroid cancer, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s disease, hyperthyroidism, and hypothyroidism can be made with the aid of these tests. Blood tests, imaging tests, and nuclear medicine tests are some examples of thyroid test types.
What are thyroid tests?
Thyroid tests Verify that your thyroid gland is functioning properly. A butterfly-shaped gland in your neck called the thyroid is located just above the sternum, or breastbone. It produces hormones that regulate numerous body processes. Your body’s use of energy is controlled by what seems to be a command center.
If you experience symptoms like fatigue, restlessness, irritability, or unexplained weight changes, you may require a thyroid test. Thyroid tests can aid in the diagnosis of conditions like:
Hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism.
Thyroiditis.
Graves’ disease.
Hashimoto’s disease.
Types of thyroid tests
Thyroid tests come in a variety of forms, but they all fall into one of two categories:
• Thyroglobulin, antibodies, and other proteins are screened for in thyroid blood tests. You can find out if you have diseases like hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid) thanks to these tests. TSH, T3, T4, thyroid antibodies, and other blood tests for the thyroid gland are available.
• Thyroid imaging tests assist your doctor in locating nodules (lumps) in your neck and identifying their malignant (cancerous) or benign (noncancerous) nature. This category includes nuclear medicine imaging tests like thyroid uptake and scans. (For these tests, a tiny amount of contrast material is either injected or swallowed.)
How do thyroid blood tests work?
Various hormones and antibodies are detected in your blood during thyroid blood tests. You may have thyroid disease if you have too many or too few of these hormones or antibodies.
Different blood tests are used by providers to assess various factors, including:
Your thyroid-stimulating hormone is measured by TSH. Most providers typically suggest this test as the first one. The brain’s pituitary gland produces TSH in your body. Your thyroid gland receives it and is stimulated to produce the thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
T3, also known as free T3, is a test for triiodothyronine levels in the body. One of the two main hormones produced by your thyroid is this one.
T4 (or free T4) measures the amount of thyroxine in your blood. Thyroxine is the other main type of hormone that your thyroid makes.
Thyroid antibody tests tell your provider whether or not there are thyroid antibodies in your blood. The presence of thyroid antibodies might mean you have an autoimmune disorder like Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s disease.
How to prepare for your thyroid blood test?
In general, there isn’t anything special you have to do before your test. Unless your healthcare provider advises otherwise, you are free to consume food and drinks normally.
What should you expect during your thyroid blood test?
Your blood will be sampled during a thyroid blood test and sent to a lab for evaluation. The lab will send the test results to the ordering provider as soon as they are completed.
What to expect after your thyroid blood test?
Your healthcare provider will discuss their findings with you. They might recommend additional testing if they need more information. They’ll tell you what your results mean and what comes next.
How do thyroid imaging tests work?
Your doctor can learn more about the size, shape, and function of your thyroid gland from thyroid imaging tests. After you’ve had thyroid blood tests, providers may advise imaging tests.
Different imaging tests are used by healthcare providers for different reasons:
· The size, position, and shape of your thyroid gland can be determined using a thyroid ultrasound by using sound waves. A medical professional applies a handheld device to the skin of your neck during this test. When the soundwaves bounce off your thyroid, the device sends them through your body, and a receiver analyzes the soundwaves. Ultrasound is used by healthcare providers to detect neck lumps (nodules).
· Thyroid scans use computed tomography (CT) to look at the size and position of your thyroid gland. In most cases, your provider will use contrast material to highlight areas of concern. Contrast materials block the amount of X-rays that go through your body and help get detailed pictures. This involves either an injection of radioactive iodine in your vein or a capsule that you swallow prior to the test. Sometimes providers take thyroid scans without contrast material, but it’s less common.
· Thyroid Tests uptake Let your doctor know how well your thyroid functions. You will ingest a small amount of radioactive iodine (in liquid or pill form) four to six hours prior to the test. Your doctor will place a gamma probe in front of your neck as you sit in a chair for your appointment. (A gamma probe is a portable instrument that gauges the amount of iodine your thyroid assimilates from your blood.) This process only takes a few minutes and is not painful. A second reading will typically be taken by your doctor 24 hours later. You may have hyperthyroidism or Graves’ disease if your thyroid absorbs a lot of iodine.
How do you prepare for your thyroid imaging test?
If your healthcare provider plans to use a contrast material, you might need to stop eating or drinking for a few hours before your procedure. Or, you might need to avoid kelp and other foods with a high iodine content.
Instructions will vary depending on your situation. Your provider will tell you if you need to make any special preparations.

What should you expect after your thyroid imaging test?
The physician who ordered the test will receive your imaging results from your radiologist. They will review your scans and then review their findings with you before making any recommendations.
Your doctor may recommend a needle biopsy, also known as an FNA (fine needle aspiration) procedure, if your scans show a lump on your neck. They will be able to determine from this whether the lump is cancerous or not.
When should I know the results of my thyroid test?
Once your provider reviews your thyroid test results, they’ll call you to discuss them or schedule a follow-up office visit. In most cases, this process should only take a few days.
What blood tests show thyroid function?
To evaluate thyroid function, medical professionals may perform several types of blood tests, for Thyroid Tests.. TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and T4 or free T4 (thyroxine) levels are checked by the two most common tests.
A full thyroid blood test panel may also be recommended by providers.
What is included in a full thyroid panel?
A full thyroid blood test panel measures the levels of these hormones and antibodies in your blood:
· TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone).
· T3 or free T3 (tri-iodothyronine).
· T4 or free T4 (thyroxine).
· TPO (thyroid peroxidase antibodies), also known as microsomal antibodies.
· TG (thyroglobulin).
· TGAb (thyroglobulin antibodies).
· TSI (thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin).
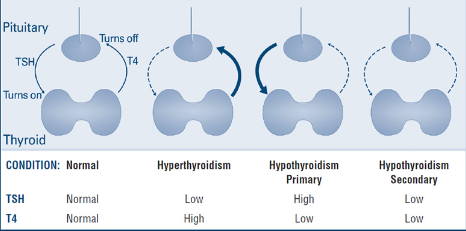
What happens if my TSH level is high?
If your TSH level is high, it might mean you have hypothyroidism. This means your thyroid gland doesn’t make enough thyroid hormone.
On the other hand, if your TSH is low, it could indicate hyperthyroidism. In this case, your thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone.
Your healthcare provider will discuss your results and tell you what they mean for you and your health.
What can affect thyroid test results?
There are certain things that can throw off your thyroid test results, including:
- Certain medications and supplements.
- The time between the last time you took your thyroid medication and when a provider draws your blood. (This is only a factor when you’re taking thyroid medication that contains T3.)
- Whether you ate before your test (only a factor with thyroid scans).
- Stress, including the effects on a non-thyroidal illness.
Do you have to fast for a thyroid test?
Depending on the test you are taking. Most medical professionals advise against fasting before a thyroid blood test. However, you might need to stop eating and drinking a few hours prior to your appointment if you need to have a thyroid scan, particularly one that requires a contrast material.
If you need to fast or take any other precautions before your thyroid test, your doctor will let you know.
A note for all persons
An overactive and underactive thyroid can interfere with daily routines and hinder your quality of life. If you have symptoms of thyroid disease, a thyroid test can find out what’s causing them, so your provider can recommend treatment.


